Discover the true cost of post-weaning Diarrhoea
Post Weaning Diarrhoea (PWD) will affect the majority of UK pig herds1 and costs up to £5 per piglet.2,3
A common cause of post-weaning diarrhoea (PWD) are two specific types of disease-causing E. coli strains known as F4/F18 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.4,5
Historically before its ban, zinc oxide had masked the undesirable effects of PWD among many pigs. Now producers are looking for alternative methods to control PWD.
Knowing what is causing post-weaning diarrhoea (PWD) on your farm is vitally important to help determine the best PWD prevention strategy.
If E. coli F4/F18 is responsible for PWD on your farm, vaccination with Coliprotec™ F4/F18 can:
- Reduce the incidence of PWD6
- Reduce the risk of PWD by reducing faecal shedding of E. coli F4/F18 from infected pigs6
- Improve productivity of piglets2,7-9
Coliprotec™ F4/F18 vaccinated piglets:
Weigh 1 kg or more at the end of nursery2,7
Deliver 2 kg of additional slaughter weight8
Reach market weight up to 7 days sooner9
Receive substantially less medication during the nursery period9
Request your on farm E. coli test kit
Simply click below to request a FREE E. COLI TEST as soon you observe symptoms (typically in the first three weeks immediately after weaning).
This simple to use test comes with full instructions on how to use the test and a booklet for further support around PWD on your farm.
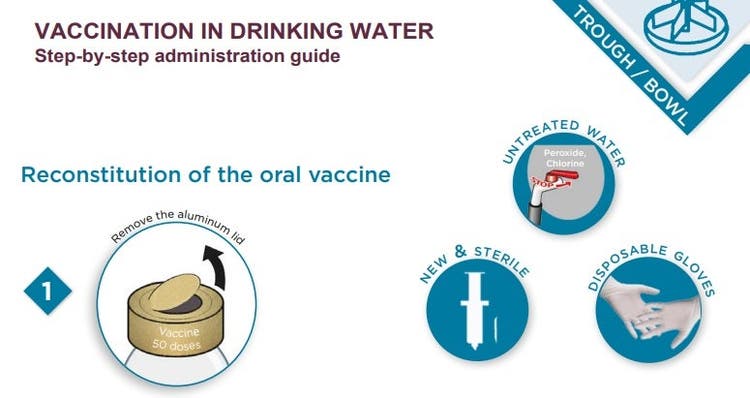
Vaccination in Drinking Water
A step by step administration guide for before and after weaning. (PDF)
Rainbow Test Kits Guide
Learn how to use the Rainbow Piglet Test Kits, which test for E. coli F4/F18, Rotavirus and Clostridium perfringens. (PDF)

Coliprotec Digital Detailer
Coliprotec vaccine can be a sustainable way to prevent PWD and how to register for Elanco's free E. coli diagnostic testing service. (PDF)

Coliprotec Producer Guide
From Faecal Scores to Coliprotec storage and administration, a PWD management guide. (PDF)
- Farmers Weekly Post Weaning Diarrhoea Research 2020.
- Elanco. Data on file. Elanco study ELA 1700757 report 2018.
- Tokach, L.M. et al. 2000. Swine Health & Production; 8: 229-233.
- Fairbrother JM and Gyles LG, 2012. Colibacillosis. In: Diseases of Swine. Zimmerman JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, Schwartz KJ and Stevenson GW. Editors. 10th Edition. John Wiley and Sons, Inc. Chapter 53, p 723-749.
- Luppi, A. et al. 2016. Porcine Health Management, 2:20. DOI: 10.1186/s40813-016-0039-9.
- Coliprotec F4/F18 lyophilisate for oral suspension for pigs summary of product characteristics (SPC)
- WHO 2017 – Guidelines on use of medically important antimicrobials in food-producing animals –https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/258970/978924155013-eng.pdf%3bjsessionid=B982A811C8A4F2F79F5C306E2B647D62?sequence=1
- Purina Mills Report. Each production phase impacts the next:
- Vangroenweghe, F. et al., 2018. Proceedings of the 10th ESPHM: 252.
